

Services
Smart, AI-powered solutions to streamline compliance and enhance workplace safety. Stay compliant with ease and efficiency.


Occupational Health and Safety Management In Action
By Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) into the monitoring and checking processes of ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems) can greatly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and real-time capabilities of managing health and safety at the workplace. Here's are some of the revolutionary real time compliance benefits:
1. Real-time Hazard Detection
Sensors for Environmental Hazards: IoT-enabled sensors can monitor environmental factors like temperature, humidity, gas levels (e.g., CO2, methane, etc.), air quality (e.g., particulate matter), and noise levels. These are crucial for preventing occupational health issues, especially in industries like manufacturing, mining, or construction.
Example:
Smart sensors could be placed in areas prone to high heat or toxic fumes, automatically triggering alarms or notifying safety officers when conditions exceed acceptable thresholds.
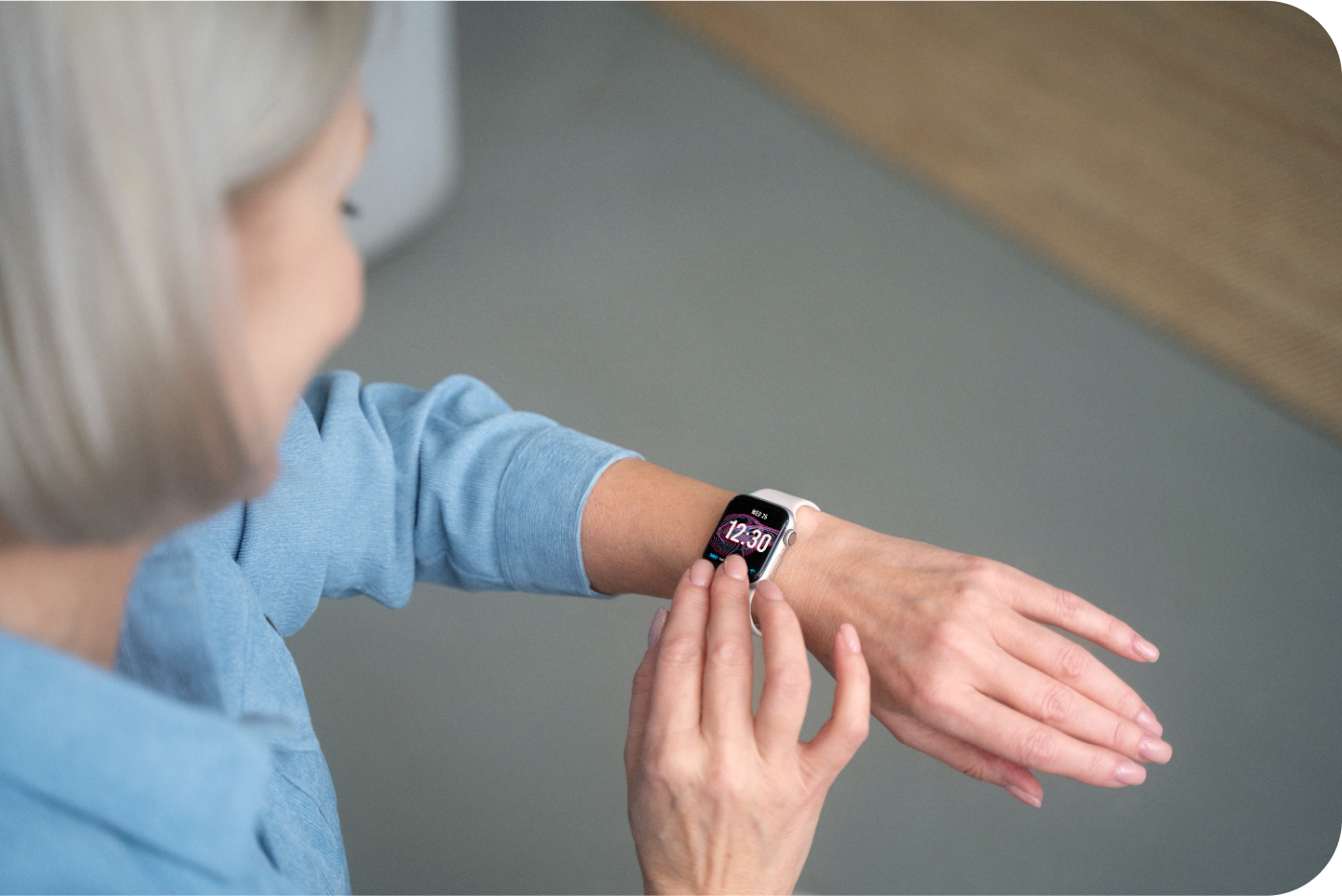


2. Employee Health Monitoring
Wearables for Health Data: IoT wearables (such as smart helmets, vests, or wristbands) can track workers' physiological parameters like heart rate, body temperature, fatigue levels, and even their location within the facility.
Example:
If a worker's heart rate rises to an unsafe level due to heat stress, or if they are entering a high-risk zone, the system can alert supervisors to take immediate action.
3. Equipment and Machinery Monitoring
Predictive Maintenance: IoT can monitor the status of machinery and equipment, detecting malfunctions or wear-and-tear that could lead to accidents. This enables predictive maintenance, reducing the likelihood of failure and potential injuries.
Example:
Vibration sensors or temperature monitors on machines can alert maintenance teams about potential issues before they cause a breakdown or safety hazard.
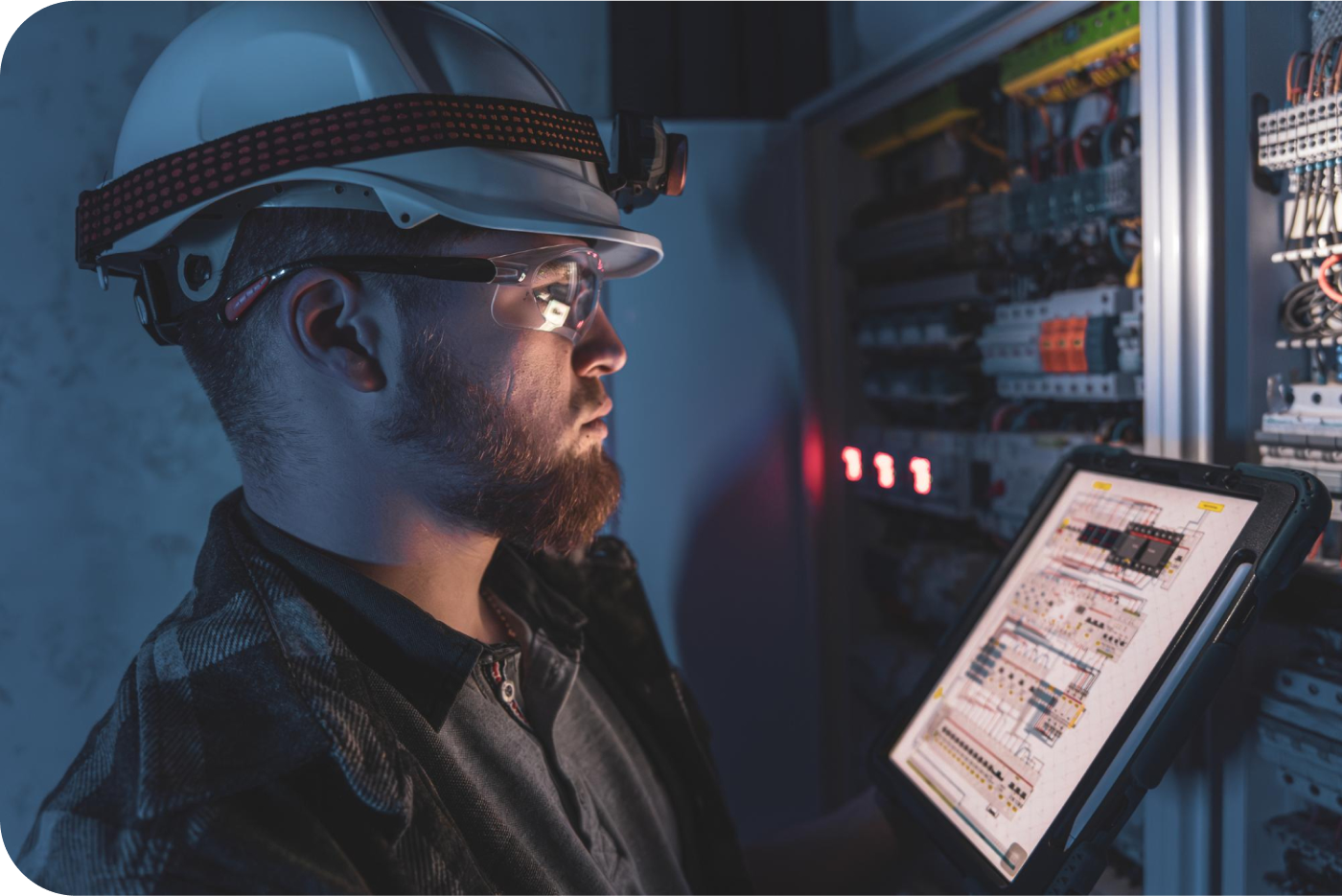


4. Tracking Safety Compliance
Document Control and Workflow Automation: IoT systems can integrate with enterprise software to ensure that safety protocols, inspections, and risk assessments are being completed as required. RFID tags, for example, can be used to track the movement of safety equipment and ensure that workers have access to and are using the correct personal protective equipment (PPE).
Example:
When a worker enters a hazardous area, the IoT system can check that they are equipped with the correct PPE (e.g., helmet, gloves, safety goggles) before granting access.
5. Incident Reporting and Response
Automated Incident Detection and Reporting: IoT systems can detect specific events that could lead to accidents, such as slips, falls, or equipment malfunctions. Once detected, the system can automatically log the incident, alert relevant personnel, and initiate predefined response protocols.
Example:
A fall detection system could immediately notify the nearest safety officer or trigger an alarm if a worker falls in an area with high-risk activities.
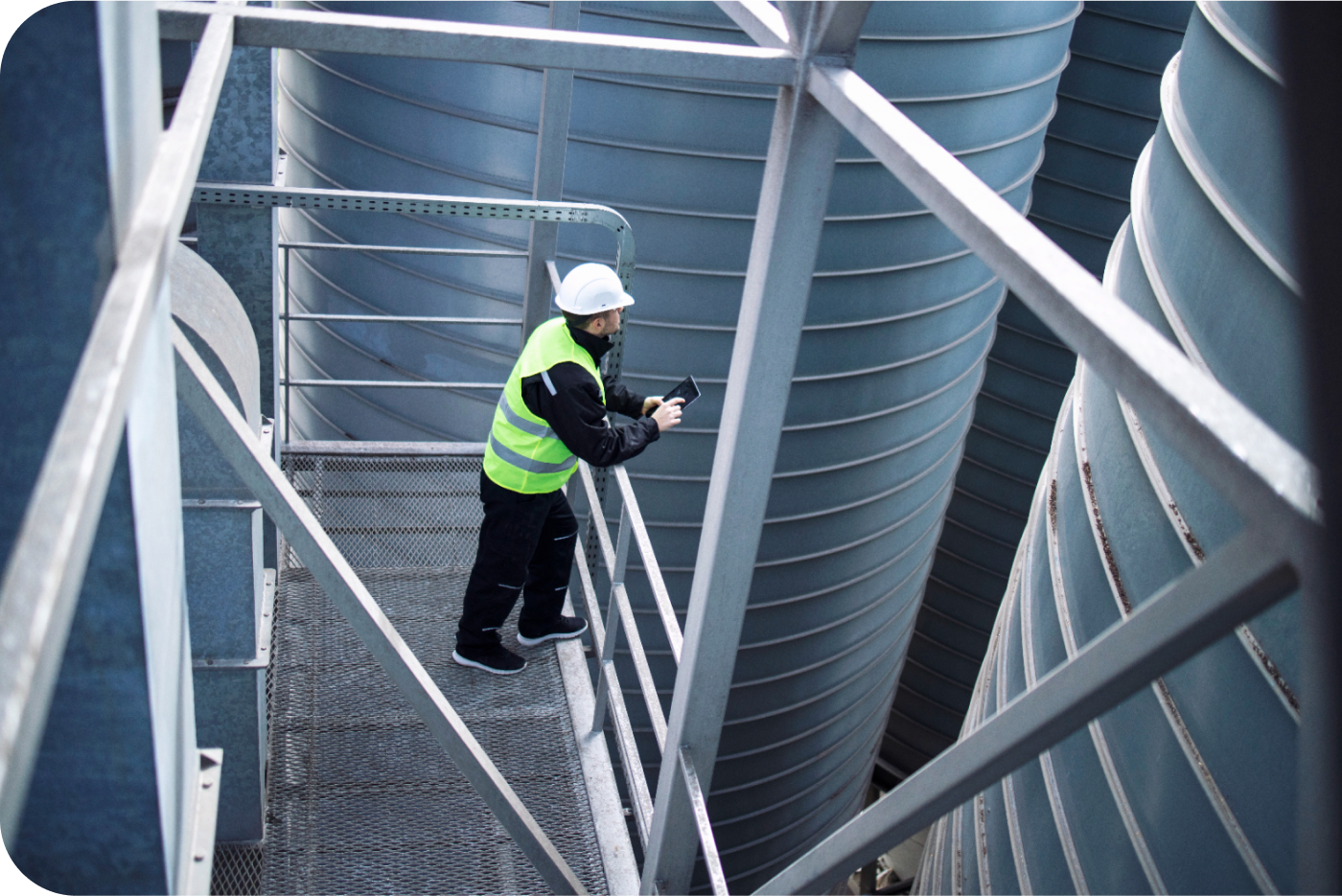


6. Continuous Safety Auditing and Data Logging
Continuous Monitoring for Audits: Data collected by IoT devices (such as temperature, humidity, machine status, and worker activity) can be automatically logged and analyzed to ensure that the organization is consistently meeting the standards of ISO 45001.
Example:
IoT systems can log real-time data for audit trails, providing evidence for compliance with safety regulations and internal safety audits without needing manual data entry.
7. Employee Behaviour Analysis
Behavioural Analytics: IoT-enabled systems can analyze workers' behavior in real-time and provide insights into risky behavior patterns. For example, analyzing motion data from wearables can help identify when workers take shortcuts or avoid proper safety procedures.
Example:
If a worker consistently enters a dangerous zone without following safety protocols, the system can issue a warning or send a corrective action notification to the supervisor.


8. Training and Simulation
Immersive Safety Training: Virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) devices, integrated with IoT sensors, can provide workers with immersive safety training experiences. These IoT-powered training simulations can replicate real-life hazardous scenarios and ensure that employees are better prepared for emergencies.
Example:
A worker might practice responding to a fire alarm in a simulated environment where IoT sensors trigger smoke, temperature, and sound effects to simulate a real emergency situation.
9. Remote Monitoring and Control
Monitoring Safety Conditions from a Distance**: IoT technologies enable remote monitoring of work environments. Safety managers or supervisors can track key parameters (e.g., gas concentrations, temperature, air quality) remotely in real time and take necessary actions without being physically present on-site.
Example:
Supervisors in an office can monitor hazardous zones in a manufacturing plant or construction site through IoT-connected cameras and environmental sensors, ensuring safety measures are being adhered to.

10. Integration with ISO 45001 Processes
Risk Assessment:
IoT data can feed into the risk assessment process, identifying emerging hazards that might not have been previously considered. This data-driven approach allows for more precise and up-to-date hazard analysis.
Management Reviews:
The data collected from IoT systems can be used in management review meetings to assess the effectiveness of the health and safety management system. This can include evaluating trends in safety incidents, employee health, and the operational performance of safety equipment.
11. Compliance with ISO 45001 Clauses
IoT integration can support compliance with several key clauses of ISO 45001:
Clause 4 (Context of the Organization):
IoT systems can help identify external and internal factors that might impact worker health and safety, such as environmental factors or new machinery.
Clause 5 (Leadership and Worker Participation):
IoT can help ensure that leadership and workers are actively engaged in safety monitoring by providing them with real-time actionable data.
Clause 6 (Planning):
Data from IoT systems can assist in identifying hazards, assessing risks, and defining control measures for continuous improvement.
Clause 8 (Operation):
Continuous monitoring and data feedback help manage operational health and safety performance, ensuring the effectiveness of controls and procedures.
Benefits of IoT Integration for ISO 45001:
Improved Safety:
Real-time monitoring allows for faster detection and response to safety hazards, reducing risks of accidents.
Increased Efficiency:
Automation of monitoring and reporting processes reduces administrative burden and allows safety officers to focus on critical tasks.
Data-Driven Insights:
Continuous data collection enables deeper insights into health and safety performance, leading to more informed decision-making and more accurate risk assessments.
Cost Savings:
By preventing accidents and reducing equipment downtime through predictive maintenance, organizations can save costs in the long term.
In conclusion, integrating IoT technologies into the ISO 45001 framework offers a powerful way to enhance workplace health and safety management, providing real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and increased operational efficiency. This can help organizations not only comply with the standards but also create a safer, more responsive work environment.
